Nanoparticles & Beads Conjugation
Service Description
Relying on our state-of-the-art chemical biology facilities and years of combined experience in providing high-quality bioconjugate complexes, BOC Sciences is capable of conjugating a wide range of different biomolecules with nanoparticles and beads. We use the highest quality nanoparticles and beads when applying our proprietary conjugation protocols to provide optimized products and meet your assay needs. Specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility are defined to meet your absolute expectations for conjugates.
What are Nanoparticles & Beads?
Nanoparticles are manufactured microscopic particles with sizes up to 100 nm. Semiconductor nanoparticles smaller than 10 nm are also known as quantum dots due to their quantized electronic energy levels. Nanoparticles may be in the form of emulsions, polymers, ceramic particles, metal particles, and carbon particles. Moreover, nanoparticles are of great scientific research value, bridging the gap between large pieces of matter and atoms and molecules. The physical properties of large pieces of matter are usually independent of size, but this is not the case at the nanometer size, and liposomes are typical nanoparticles with solid-like properties.
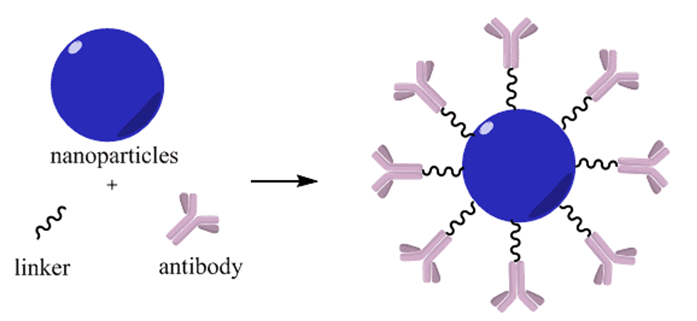 Fig. 1 Nanoparticle-antibody conjugation.
Fig. 1 Nanoparticle-antibody conjugation.
Beads are superparamagnetic microspheres with fine particle size. They can gather rapidly in a magnetic field and disperse uniformly when they lead the field contributing to magnetic separation. Some applications of beads include conjugating to drugs, proteins, enzymes, antibodies, or nucleic acids.
 Fig. 2 Schematic of magnetic on-bead antibody conjugation using (A) thiols on cysteine residues and (B) amines on lysine residues (Nath N, 2015)
Fig. 2 Schematic of magnetic on-bead antibody conjugation using (A) thiols on cysteine residues and (B) amines on lysine residues (Nath N, 2015)
Applicaiton of Nanoparticles & Beads Conjugation
- Flow cytometry/fluorescence microscope
- Immunochromatographic test strip/test
- Agglutination test/detection
- Calibration/verification
- Cell separation
- Nucleic acid purification
- Protein purification
- Proximity detection
- Instrument QC
- Magnetic particle analysis
- Molecular diagnostics
- Targeted therapeutics
- Improved toxin/pathogen testing
- Molecularly-resolved medical imaging
Our Advantages
- Advanced equipment and techniques
- Experienced scientific team
- Advanced Enzyme Labeling platform
- Highly reliable and reproducible results
- Spacer between nanoparticles and conjugated ligands
- Detailed data analysis and report with results and discussion
- Quality one-stop and flexible service options
Project Workflows
Can't find the type of service you need? Don't worry. We provide comprehensive bioconjugation services that extend beyond the described service portfolio. Simply contact us with your detailed project descriptions. In most cases, we can accommodate your bioconjugation needs!
Quality Services
| Our Services | Types of Biomolecules | Type of Macroparticle and Nanoparticle |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
It refers to the process of attaching nanoparticles or beads to molecules like proteins, peptides, or oligonucleotides, enabling better detection and manipulation in various applications.
This technique is widely used in diagnostics, immunoassays, drug delivery systems, and biosensors for improved sensitivity and specific targeting.
Yes, we offer customizable conjugation services where you can select bead types, functional groups, and other parameters to suit your specific research needs.


References
- Uga H; et al. A new mechanism of methotrexate action revealed by target screening with affinity beads. Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Nov; 70(5): 1832-9.
- Nath N; et al. On-bead antibody-small molecule conjugation using high-capacity magnetic beads. J Immunol Methods. 2015 Nov; 426: 95-103.