GalNAc-siRNA Conjugation
As a leading CRO, BOC Sciences offers custom GalNAc-siRNA conjugation service to support our clients' research and development needs. With our expertise in drug conjugation, we are committed to providing high quality and reliable services to accelerate the development of novel siRNA-based therapeutics.
Why Conjugated siRNA?
RNA interference (RNAi) has emerged as a powerful tool for gene regulation and therapeutic intervention. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are the key players in RNAi, which can specifically target and degrade messenger RNA (mRNA) of a target gene. However, the therapeutic application of siRNAs is limited by their instability, poor pharmacokinetic properties, and inability to effectively reach target tissues. To overcome these limitations, siRNAs need to be further modified to improve their drug delivery efficiency.
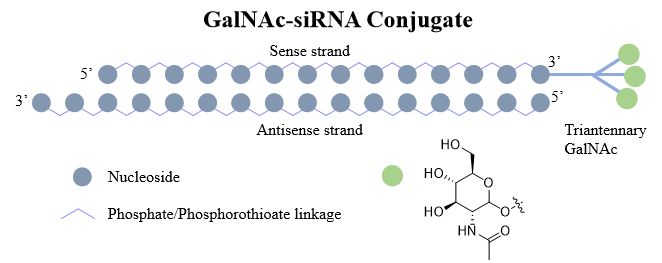
What are GalNAc-siRNA Conjugates?
GalNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine) is a sugar molecule that can be utilized as a ligand for the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR), a liver-specific receptor expressed on hepatocytes. It's worth noting that GalNAc is a naturally occurring sugar molecule in the body and is therefore less likely to trigger an immune response compared to other drug delivery vehicles. By conjugating siRNA molecules with GalNAc, the resulting GalNAc-siRNA conjugates are able to target hepatocytes with high specificity and efficiency. GalNAc-siRNA conjugates are taken up by hepatocytes via the ASGPR-mediated endocytosis, follow by undergoing intracellular processing and release of the siRNA molecules, which then bind to their complementary mRNA targets, leading to mRNA degradation and gene silencing.
Our GalNAc-siRNA Conjugate Services
siRNA Design
Effective siRNA design is critical for the success of GalNAc-siRNA conjugates. Our team of experts can design siRNAs that target specific genes of interest, using advanced algorithms and databases. We also perform in silico analysis to assess the specificity and efficacy of the siRNAs.
Conjugation and Purification
We use a variety of conjugation chemistries to covalently attach GalNAc to the siRNA molecule, including thiol-maleimide reaction, click chemistry, amine-carboxylic acid reaction, and thiol-ene reaction. After conjugation, we purify the GalNAc-siRNA conjugates using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or other purification methods, to remove any unreacted reagents or impurities.
Characterization
We perform extensive characterization of our GalNAc-siRNA conjugates to ensure batch-to-batch consistency. This includes assessing the purity, identity, and integrity of the conjugates, as well as evaluating their stability and pharmacokinetic properties.
Advantages of GalNAc-siRNA Conjugates
- Improved pharmacokinetics: GalNAc conjugation can increase the half-life of the siRNA molecule in the bloodstream by protecting it from degradation by nucleases. This can lead to more sustained and efficient delivery of the siRNA to target tissues.
- Enhanced cellular uptake: The GalNAc moiety targets the siRNA to hepatocytes, which express high levels of the ASGPR. This leads to enhanced cellular uptake of the siRNA conjugate and improved target gene silencing.
- Reduced off-target effects: The specificity of GalNAc-siRNA conjugates for hepatocytes can reduce off-target effects of the siRNA molecule on other tissues.
- Lower doses: GalNAc conjugation can allow for lower doses of the siRNA to be administered, since the conjugate is more efficient at reaching its target and inducing gene silencing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
GalNAc is used for its ability to specifically target asialoglycoprotein receptors (ASGPR) on liver cells. This targeting increases the efficiency of siRNA delivery to the liver, ensuring higher levels of gene silencing while minimizing off-target effects.
By conjugating siRNA with GalNAc, the conjugates are more efficiently recognized and internalized by liver cells, leading to increased RNA interference activity. This targeted delivery ensures that the siRNA reaches its intended site of action with minimal degradation or loss of activity.
The GalNAc-siRNA Conjugation process is scalable, using established conjugation techniques and large-scale production methods. This ensures that conjugates can be produced at both research and commercial scales with high purity and consistency.

