Antibody Conjugation Services
High-performance Site-specific Conjugation GMP-grade
BOC Sciences provides personalized antibody conjugation services to support research and development in the field of antibody drugs. As a leading service provider of bioconjugation, our antibody conjugation services include antibody conjugated PEG, biotin, fluorescence dye, enzyme and oligonucleotide, which have been proven to improve the function and performance of antibody drugs, as well as to use for imaging and detection. Furthermore, antibody-drug conjugation services are provided to support the forefront of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) development.
What is Antibody Conjugation?
Antibody-based drugs have become an important class of biological drugs. The monoclonal antibody (mAb) and its derivatives, such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), bispecific antibodies, have been widely used in the effective treatment of human diseases, particularly in the fields of immunology and oncology. In antibody-based therapy, various antibody derivatization approaches are used to improve the performance of antibodies or to test antibody drugs. For instance, the conjugation of PEG to antibodies can enhance the solubility of antibodies, reduce immunogenicity, and increase the circulating half-lives of antibodies. In addition, exploiting the character of antibodies binding specifically to antigens, antibodies labeled with chromogenic agents, such as fluorophore, enzyme, biotin, etc., provides a tool for the localization, characterization and quantification of antigens in biological tissues. With increased understanding of immunobiology and the continued development of molecular biology methods, it is believed that the possibilities of antibody-based therapeutics are bounded only by the scope of human ingenuity.


Our Antibody Conjugation Services
PEG conjugated antibodies offer reduced immunogenicity, enhanced solubility, stability and improved bioavailability compared to prototype antibodies while retaining the maximum biological activity.
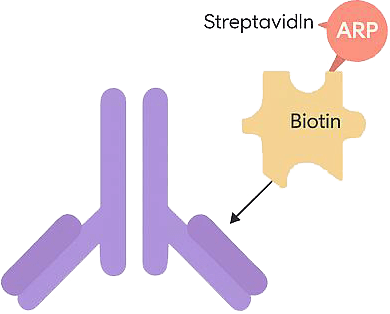
Biotin-labeled antibodies are endowed with strong affinity for streptavidin and avidin, which can be used in histocytochemistry, immunoassays, and fluorescence-based flow cytometry.
Fluorophore-labeled antibodies retain antibodies activity and exert additional fluorescent tracer effects. Fluorescent dyes, including FITC, rhodamine, cy3, cy5, etc., can be used to label antibodies.
Antibody labeling antibodies is mainly used for antigen localization analysis. Various reporting enzymes, such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and many other enzymes, can bind to antibodies.
Antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates (AOCs) have been widely used in many diagnosis and treatment applications, such as biomarker discovery, clinical diagnosis, and protein-protein interactions.
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) combine the monoclonal antibodies targeting capability and cancer-killing of cytotoxic drugs, can target cancer while minimizing exposure to healthy tissue.
Antibody-Cell Conjugation is a bioconjugation technique that covalently links antibodies to cell surfaces, used for targeted cell therapies or enhancing immune cell functions.
Antibody glycosylation is the process of adding sugar molecules to an antibody, influencing its stability, efficacy, and immune response.
Antibody-Liposome Conjugation is a technique that attaches antibodies to liposomes, enabling targeted delivery of drugs or therapeutic agents to specific cells or tissues.
Antibody-Polymer Conjugate is a bioconjugate where antibodies are linked to synthetic polymers, enhancing drug delivery, stability, and targeting of therapeutic agents.
Antibody-Antibiotic Conjugation is a technique that attaches antibiotics to antibodies, enabling targeted delivery of antibiotics to specific pathogens or infected cells.
Antibody-Biopolymer Conjugation is the process of linking antibodies to biopolymers, enhancing the targeting, stability, and controlled release of therapeutic agents.
Antibody-Exotoxin Conjugation is a method that links antibodies to exotoxins, enabling targeted delivery of the toxin to specific cells or tissues for therapeutic or cytotoxic purposes.
Antibody-Photosensitizer Conjugation is the process of attaching a photosensitizer to an antibody, enabling targeted photodynamic therapy for precise destruction of cancer cells or pathogens upon light activation.
Antibody-PNA Conjugation is the technique of linking antibodies to peptide nucleic acids (PNAs), enabling targeted delivery of PNAs for gene modulation or therapeutic applications.
Antibody-siRNA Conjugation is the process of attaching small interfering RNA (siRNA) to antibodies, allowing targeted delivery of siRNA to specific cells for gene silencing and therapeutic purposes.
Degrader-Antibody Conjugation is a technique that links targeted protein degraders to antibodies, enabling selective degradation of specific proteins in targeted cells for therapeutic applications.
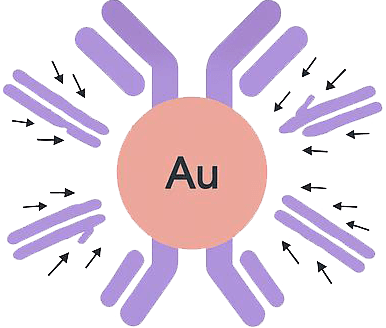
Gold Nanoparticles-labeled Antibody is a conjugate where gold nanoparticles are attached to antibodies, enhancing imaging, detection, and targeted therapeutic applications.
Immune-Stimulating Antibody Conjugation is the process of linking antibodies to immune-stimulating agents, enhancing immune responses for targeted cancer therapy or infectious disease treatment.
Luminex Bead Labeled Antibody is a technique where antibodies are attached to Luminex beads, enabling the simultaneous detection and quantification of multiple analytes in biological samples using a multiplex assay.
Magnetic Beads-labeled Antibody is a technique where antibodies are conjugated to magnetic beads, allowing for the isolation, enrichment, or detection of specific targets in biological samples using a magnetic field.
Molecular Glue–Antibody Conjugate is a bioconjugate that links antibodies to molecular glue compounds, facilitating targeted protein degradation by promoting the interaction between specific proteins for therapeutic applications.
Protein-Antibody Conjugation is the process of attaching a protein to an antibody, enabling targeted delivery or detection of the protein for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes.
Silver Nanoparticles-labeled Antibody is a conjugate where antibodies are attached to silver nanoparticles, enhancing detection, imaging, and therapeutic applications through the unique properties of silver.
Antibody-ASO conjugates combine the high specificity of monoclonal antibodies with the gene-silencing power of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs). By linking ASOs directly to targeted antibodies, this technology enables precise delivery of oligonucleotide therapeutics to specific cells or tissues, enhancing efficacy and minimizing off-target effects. Ideal for targeted RNA modulation, precision medicine, and next-generation bioconjugate drug development.
An antibody-streptavidin conjugate leverages the strong biotin-streptavidin interaction for high-affinity detection, purification, and assay development. These conjugates ensure reliable signal amplification and compatibility with various biotinylated reagents, making them essential tools in ELISA, flow cytometry, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. Optimized conjugation preserves antibody activity and provides consistent, reproducible results for diagnostic and research applications.
PROTAC-antibody conjugates integrate targeted protein degradation with antibody-mediated delivery. By combining PROTAC molecules with antibodies, this advanced platform allows for cell-specific degradation of disease-causing proteins, expanding therapeutic possibilities beyond traditional inhibitors. These bioconjugates are at the forefront of next-generation biologic therapeutics and targeted degradation drug discovery.
Antibody-HRP (horseradish peroxidase) conjugation provides sensitive and stable enzyme labeling for a wide range of immunoassays. Using optimized coupling chemistry, antibodies are linked to HRP without compromising antigen affinity, ensuring strong signal generation and low background. Ideal for ELISA, Western blot, and immunohistochemical staining, our antibody-HRP conjugation service guarantees high-purity, high-performance immunoreagents for research and diagnostics.
Antibody-RNA conjugates enable targeted RNA delivery by coupling RNA molecules—such as mRNA, siRNA, or aptamers—to antibodies that specifically recognize surface markers. This innovative platform allows precise nucleic acid delivery into selected cell types, supporting RNA therapeutics, vaccine development, and cellular imaging applications. Each conjugate is carefully engineered for stability, biocompatibility, and functional efficiency.
From Inquiry to Completion: Our Service Flow

Advantages of Working with Us
- Profound knowledge and extensive experience in antibody conjugation
- Comprehensive antibody conjugation service and leading antibody technology
- People and suites that specialize in ADC development, manufacturing and testing
- High levels of antibody recovery so to save your precious reagents
- Full technical support
- Reliable and reproducible result
- Detailed report and data analysis, including results and discussion
Where Our Antibody Conjugation Are Used?
Diagnosis Field
Immunoassay: After labeling with fluorescent dyes, enzymes, and other markers, antibodies can be used in ELISA, immunofluorescence, chemiluminescence immunoassays, etc., to detect antigens or antibodies in samples, such as tumor markers, hormones, viral antigens, and more.
Flow Cytometry: Fluorescently labeled antibodies can be used in flow cytometry to quantitatively analyze cell surface antigens, differentiate various cell populations, and study the immune phenotype and differentiation level of cells. It is widely used in hematological disease diagnosis and immune function evaluation.
Immunohistochemistry: By conjugating antibodies with fluorescent dyes, enzymes, and other markers, tissue sections or cell smears can be stained to locate and quantitatively detect specific antigens in tissues or cells. It is used in pathological diagnosis, tumor staging, and more.
In Situ Hybridization: After conjugating antibodies with nucleic acid probes, it can be used to detect specific nucleic acid sequences in tissues or cells, such as detecting the localization of viral DNA or RNA in cells, enabling early disease diagnosis.
Therapeutic Field
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC): Antibodies are conjugated with cytotoxic drugs, where the antibody specifically recognizes and binds to antigens on tumor cells, delivering the drug precisely to the tumor cells, exerting anti-tumor effects. An example is the already marketed trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla), used to treat HER2-positive breast cancer.
Radioimmunotherapy: Antibodies are conjugated with radioactive isotopes, using the radiation produced by the isotopes to kill tumor cells, while the targeted nature of the antibody minimizes damage to normal tissues. An example is iodine-131-labeled anti-thyroglobulin antibodies used in thyroid cancer treatment.
Biomedical Research Field
Cell Biology Research: In molecular labeling and tracing within cells, antibodies conjugated with fluorescent dyes and other markers can label specific proteins inside cells, tracking their localization, transport, and metabolic processes. It helps study intracellular signal transduction pathways, protein interactions, and more.
Molecular Biology Research: Used to study the structure and function of proteins, for example, conjugating antibodies with biotin and other markers, and using affinity chromatography and other methods to isolate and purify specific proteins or conduct protein chip analysis to study protein interactions, expression profiles, and more.
Drug Development: During drug target discovery and validation, antibody conjugates can be used to detect the expression levels, distribution, and function of drug targets, evaluate the mechanisms and efficacy of drugs, and provide a basis for new drug development.
Molecular Diagnostics Field
Nucleic Acid Testing: Antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates are used in immuno-PCR to enhance the sensitivity of protein detection and quantification. Proximity ligation technology can detect single proteins or protein-protein interactions and is used in molecular diagnostics for gene testing, pathogen detection, and more.
Biomarker Detection: Using antibody conjugates to detect biomarkers in body fluids, such as proteins and nucleic acids in blood, enabling early diagnosis, prognosis assessment, and therapeutic monitoring of diseases.
Conjugation Technology Development
Development of Novel Conjugation Reagents: Research and development of new conjugation reagents and methods to improve the efficiency, stability, and specificity of antibody conjugation, expanding the application range of antibody conjugates.
Conjugation Technology Optimization: Optimizing and improving existing antibody conjugation technologies, such as optimizing conjugation reaction conditions, enhancing the loading capacity and uniformity of markers, to improve the performance and quality of antibody conjugates.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Antibody conjugates are complexes that link antibodies to other molecules (e.g., drugs, polymers, enzymes, etc.) by chemical or biotechnology. This conjugation enhances the targeting of antibodies, allowing them to more precisely identify and attack specific pathological cells or tissues.
Antibody PROTAC conjugates are an emerging form of drug that binds antibodies to PROTACs (protein degradation targeted chimeras) for the targeted degradation of specific proteins. This conjugate has potential applications in the treatment of diseases such as cancer, enhancing efficacy by targeting the removal of disease-causing proteins.
The structure of an antibody conjugate typically consists of an antibody, a linker, and a functional molecule such as a drug, polymer, or other bioactive molecule. Antibodies are responsible for target recognition, linkers regulate the stability and release of conjugates, and functional molecules are directly involved in treatment or diagnosis.

