Cholesterol-Conjugated siRNA
The development of peptide has focused on the conjugation of peptides to pharmacokinetics (PK)-enhancing moieties. One of the most common approaches to improve PK properties is to facilitate the binding of peptide drugs to plasma proteins by conjugation of peptide lead compounds with cholesterol. The main purpose of cross-linking the lipid moiety of cholesterol to a peptide is to increase the hydrophobic properties of the latter and its lipid-solubility, so that the conjugate could cross the highly lipophilic cell membrane and enter the cytoplasm.
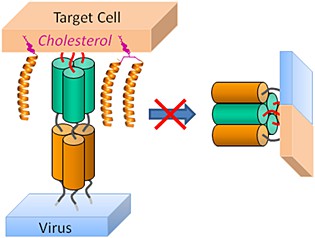 Fig 1. Cholesterol-conjugated peptide antivirals. (Pms, A. 2015)
Fig 1. Cholesterol-conjugated peptide antivirals. (Pms, A. 2015)
Application of Cholesterol-conjugated Peptide
Cholesterol-conjugate
BOC Sciences is a leading supplier of conjugates for preclinical studies. We specialize in highly modified siRNA, including conjugation to molecules such as cholesterol for cellular delivery. We will support your cholesterol-siRNA conjugation research with our expertise in high quality modified nucleic acid synthesis and excellent technical support.
What is Cholesterol-Conjugated siRNA?
Over the past two decades, significant progress has been made in the development of siRNAs as therapeutic agents. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) is the most promising RNA-based therapeutic siRNA drug. siRNA has showed promise as therapeutics in preclinical studies in non-human primates and in human clinical trials. However, the main challenge in the development of siRNA-based drugs for therapeutic use are the low efficiency of siRNA delivery to target cells and the degradation of siRNA by nucleases in biological fluids. One of the most promising approaches to solve the problem of delivering siRNA to target cells is bioconjugation; i.e., the covalent connection of siRNA to a biomolecule. Bioconjugation are "ideal nanoparticles" because they do not need to be positively charged to form complexes, are less toxic, and are less likely to be recognized by components of the immune system due to their small size. Cholesterol is considered to be the first ligand to bind siRNA because their lipophilic and endogenous transport mechanisms ensure the interaction of siRNA with cell membranes. siRNA and cholesterol derivatives can form complexes with high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) particles under certain conditions, which bind to the corresponding receptors. Therefore, this cholesterol-siRNA conjugates is considered as a universal platform for siRNA delivery throughout the body.
Advantages of Cholesterol-conjugated siRNA for Drug Delivery
- Compared with other lipophilic conjugates, cholesterol-conjugated siRNA is more efficiently retained in the body.
- After subcutaneous injection, cholesterol-conjugated siRNA can accumulate and exhibit biological activity in various tissues and organs.
- Cholesterol-conjugated siRNA does not cause immune responses or neuronal death.
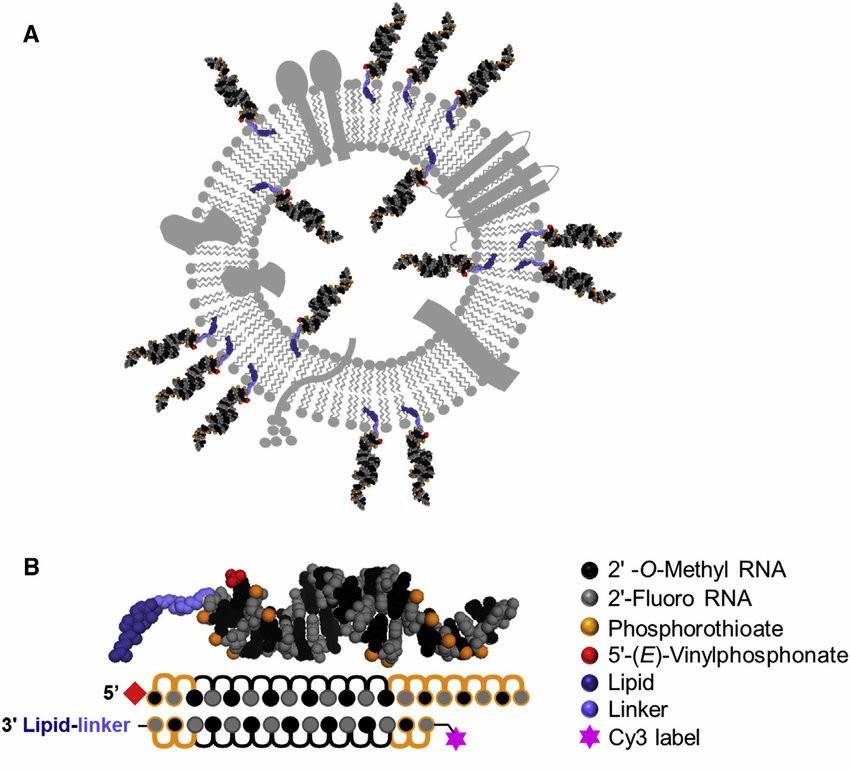 Fig 1. Representation of sEV membrane loaded with cholesterol-conjugated siRNAs. (Biscans, A.; et al. 2018)
Fig 1. Representation of sEV membrane loaded with cholesterol-conjugated siRNAs. (Biscans, A.; et al. 2018)
Synthesis Process for siRNA and Conjugates
- First, we use optimized solid-phase phosphoramidites to synthesize the sense and antisense strands of siRNAs: For 2'-O-TBDMS-protected phosphoramidites, a 10-minute coupling step is required; For 2'-O-methylated phosphoramidites, a 6-minute coupling step is required.
- The combined method of H-phosphonates and phosphoramidites is performed to synthesize 5'-cholesterol conjugates of siRNA, where cholesterol derivatives containing linkers of different lengths are converted to the corresponding H-phosphonates by interaction with phosphorus triimidazolide, followed by hydrolysis.
- Then, support-bound 5'-hydroxyl-containing sense strands of siRNA are employed for the condensation with H-phosphonates.
- At BOC Sciences, all obtained conjugates are completely deprotected with methylamine and TEA-3HF11 according to our well-established standard procedures.
- Finally, the isolation of the siRNAs conjugated to the lipophilic residues from the reaction mixture is accomplished by reversed-phase HPLC, and the purified cholesterol-conjugated siRNA is characterized by MALDI-TOF-MS and LC-ESI-MS.
Custom Cholesterol-conjugated siRNA Services
Our expert specializes in the design and production of challenging constructs as well as scaling up to mid-scale quantities. We are ready to synthesize and characterize high quality cholesterol-conjugated siRNA for research, diagnostics and therapeutics.
- Optimized synthesis and purification of siRNA.
- Each cholesterol-conjugated siRNA produced at BOC Sciences is subjected to quality control analysis by PAGE, HPLC, and/or MS.
- More customized services include additional purification and analysis, annealing, aliquoting, and formulation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Cholesterol conjugation stabilizes siRNA by improving its integration into cell membranes, boosting cellular uptake. This modification helps protect siRNA from enzymatic degradation, ensuring more effective delivery to target cells and improving overall therapeutic efficiency.
Yes, the conjugation process can be optimized to suit different types of cells and experimental conditions. By adjusting the linker structure, cholesterol concentration, and siRNA sequence, researchers can tailor the properties of cholesterol-conjugated siRNAs for specific experimental needs, such as cell type-specific delivery or improved interaction with particular cellular structures.
Cholesterol enhances the performance of siRNA by improving its membrane permeability and prolonging its half-life. The conjugation of cholesterol to siRNA allows for more targeted delivery and efficient release, optimizing the potential for specific molecular interactions in research applications.


Reference
- Biscans, A.; et al. Hydrophobicity of lipid-conjugated siRNAs predicts productive loading to small extracellular vesicles. Molecular Therapy. 2018: S1525001618301576.