Glycan
What is glycan?
Glycans are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketone polymers formed by the condensation of 10 or more monosaccharides through glycosidic bonds. They are widely present in the cell membranes and cell walls of organisms such as animals, plants and microorganisms. They not only participate in cell recognition, various life activities such as growth, differentiation, metabolism, embryonic development, viral infection, canceration, immune response, and various physiological functions such as structural support, energy storage, defense, etc., are one of the four basic substances that constitute life. A large number of studies have shown that glycans have a variety of biological activities, including antitumor, antiviral, anticoagulant, antioxidant, hypoglycemic and immunomodulatory activities. Therefore, research on glycans is becoming more important. At present, the biological activity, structure analysis and structure-activity relationship of glycans have become the focus of glycan research, and they are also the point of common concern in the field of medicine and the food and health industry.
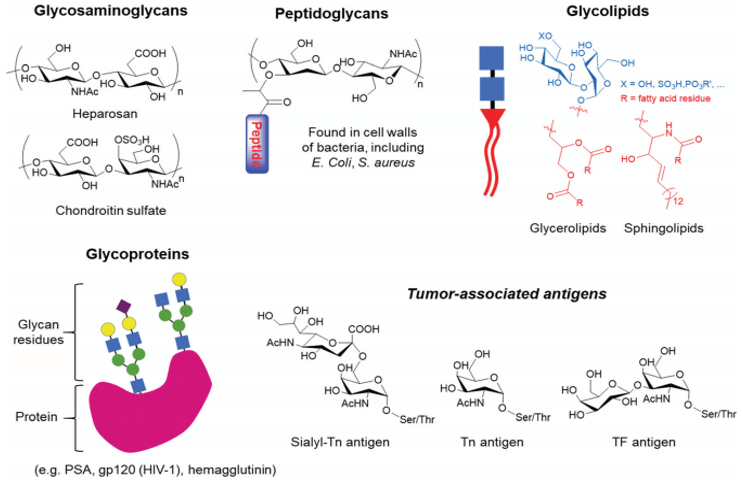 Fig. 1 Examples of glycans that can be found in nature, ranging from glycosaminoglycan polysaccharides to glycoconjugates, such as peptidoglycans, glycolipids and glycoproteins, which can bear tumour-associated antigens. (Tommasone, S., et al. 2019)
Fig. 1 Examples of glycans that can be found in nature, ranging from glycosaminoglycan polysaccharides to glycoconjugates, such as peptidoglycans, glycolipids and glycoproteins, which can bear tumour-associated antigens. (Tommasone, S., et al. 2019)
Application of Glycans
- Carbohydrate-protein conjugation: Glycan protein conjugate vaccine is a vaccine prepared by covalently binding the capsular glycans of pathogenic bacteria and the carrier protein. Glycan vaccines have poor immune effects on children, especially infants and young children. This difficulty can be overcome by coupling glycans and proteins through certain chemical means.
- Peptide glycosylation: Small molecule drug delivery system: At present, a variety of polysaccharide-peptide conjugate systems have been reported for the delivery of small molecule drugs, in which peptides are used as functional sites for targeting, and polysaccharide-based materials provide cross-linking stability and stimulation responsiveness. In addition, using amino acid differences, polysaccharide-peptide copolymers designed with specific peptide sequences play multiple roles in nucleic acid delivery, including nucleic acid concentration and endosomal escape. Tissue engineering Application of Glycans: Natural polysaccharides have good biocompatibility and water retention, as well as long polymer chains, but they are not enough to provide the functions and biological activities required by the body. The addition of peptide chains containing different functional motifs introduces a variety of specific functions for the polysaccharide scaffold. At present, a variety of polysaccharide-peptide copolymer-based scaffolds and hydrogels have been developed for tissue regeneration. Antibacterial effect: Antibacterial peptides (AMPs) are short peptides produced by living organisms that can inhibit the proliferation of microbial pathogens. Despite the ideal antibacterial activity, the high toxicity and low specificity of AMPs to mammalian cells limit their clinical Application of Glycans. For this reason, AMPs are coupled with polysaccharides with good biocompatibility and enzymatic degradation to maintain antibacterial activity while reducing immunotoxicity.
- Glycan-Coupled Folic Acid: By hydrophobically modifying natural glycans and coupling the modified glycans with folic acid, a drug carrier with a targeting effect on tumor cells can be prepared.
- Coupling with low molecular weight drugs: The most important problem of cytotoxic drugs in the treatment of malignant tumors is the systemic toxicity caused by them. This is because such drugs lack the ability to target local tumors. The above-mentioned problems can be solved by coupling biopolysaccharides and low-molecular-weight drugs.
- Fluorescently labeled glycans: Fluorescent substances have fluorescent light-emitting groups, which are bound to glycan chain molecules through chemical synthesis, so that polysaccharides have fluorescent groups for us to use common detection methods to detect. Therefore, it is useful to further understand the role of polysaccharides and study their mechanism of action.
- Sulfation modification: After the glycan is sulfated and modified, the flexibility of the sugar chain is reduced, which in turn exhibits antiviral activity. In 1988, Japanese scientific researcher Mizumoto and others successfully introduced sulfuric acid groups into some homoglycan structures for the first time and discovered that this sulfated glycan exhibited anti-T-lymphocyte virus activity. This discovery laid the foundation for sulfation to become one of the important directions of glycan chemical structure modification in the future.
- Selenization modification: Relevant experiments have confirmed that selenium glycans formed by organically combining selenium and glycans have a variety of biological activities. They can antagonize heavy metal poisoning and anti-reactive oxygen damage by increasing the activity of related enzymes, and can block DNA synthesis in cancer cells to inhibit their growth.
- Phosphorylation modification: Phosphorylation modification is one of the commonly used methods to modify the chemical structure of glycans. Like other chemical modifications, it is also a covalent modification of molecular branches. After the molecule is phosphorylated and modified, its anti-coagulation and other biological activities are significantly improved.
- Blood substitute: Glycan blood volume expanders have been widely used in clinical practice, mainly including glucosinolates (dextran) and hydroxyethyl starch (HES). The former is an α-1, 6-glucan, in the O-3 position. It contains a small amount of branches (5%); HES is obtained by modifying starch with ethylene oxide. After modification, hydroxyethyl starch is not easily hydrolyzed by amylase, so it can be retained in plasma for a long time. Based on the original oxygen-carrying molecule in the blood-hemoglobin (Hb), dextran, HES or other glycans are self-coupled with hemoglobin to achieve the functions of both oxygen delivery and plasma volume expansion.
- Immobilized carrier for cells, enzymes and other active molecules: Glycans are important immobilized carriers. Active molecules can be combined with carriers through adsorption, cross-linking and embedding. Immobilization with glycans as a carrier has the following advantages: Glycans are natural biomolecules, and its hydrophilic environment is easy to maintain the three-dimensional structure of active molecules, especially macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids, so as to maintain the original activity. Using non-toxic, non-antigenic glycans as carriers, the immobilized products formed can be directly implanted in the body to achieve specific therapeutic purposes.
- Degradable biofilm: Biofilms based on glycans have a wide range of Application of Glycans. For example, membranes made of regenerated cellulose can be used for blood analysis, plasma separation and virus removal; membranes made of chitin can be used as artificial skin or surgical threads.
- Information molecules in the body: As early as the 1970s, people discovered that sugar chains in glycoproteins can mediate signal transmission between cells. With the understanding of the biological activity and pharmacological effects of glycans, it has been discovered that the sugar chains of certain glycans also have the function of information molecules, which play a unique role in the recognition, migration and proliferation between cells
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Glycans are essential for a wide range of biological processes, including cell recognition, metabolism, immune response, and tissue development. They also play critical roles in structural support, energy storage, and protection against pathogens.
Glycans, due to their biocompatibility and water retention properties, are used in tissue engineering to create scaffolds and hydrogels. By integrating peptide chains with glycans, these materials gain additional functionalities required for tissue regeneration, supporting applications like wound healing and organ growth.
Sulfation and selenization are modifications that alter the properties of glycans, enhancing their biological functions. Sulfated glycans, for example, are known for their ability to interact with proteins and cells, while selenium-modified glycans provide protective effects against environmental stressors and oxidative damage.
Glycans are incorporated into the design of functional materials, particularly in the development of biocompatible materials for applications in environmental science and materials engineering. They enhance the properties of materials such as hydrogels, biofilms, and scaffolds, which can be used in a variety of industrial and scientific settings.


References
- Xie J H, Jin M L, Morris G A, et al. Advances on bioactive polysaccharides from medicinal plants[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2016, 56(Supp 1): S60.
- Sonnenburg, J. L., et al. "Glycan Foraging in Vivo by an Intestine-Adapted Bacterial Symbiont." Science 307.5717(2005):1955-1959.
- Yu X, Zhou C, Yang H, et al.Effect of ultrasonic treatment on the degradation and inhibition cancer cell lines of polysaccharides from Porphyra yezoensis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 117:650-656 (2015).
- Fuster, M. M., & Esko, J. D. The sweet and sour of cancer: glycans as novel therapeutic targets. Nature Reviews Cancer, 5(7), 526–542 (2005).
- Gamblin, D. P., et al. "Glyco-SeS: selenenylsulfide-mediated protein glycoconjugation--a new strategy in post-translational modification. " Angewandte Chemie International Edition 116.7(2010).
- Bosques, et al. "Effects of Glycosylation on Peptide Conformation: A Synergistic Experimental and Computational Study. " Journal of the American Chemical Society (2004).